Australian EV drivers spend 70% less money by charging EVs at home than they do by filling petrol or diesel tanks for normal internal combustion engines, and they can also access additional financial benefits. It’s a great time to purchase and own an EV!
Knowing the right information about charging EVs at home will ensure you access these cost-saving benefits. In this article, we explain the different home EV charging options.
Level 1 vs. Level 2 EV Chargers: What Is the Right Option for You?
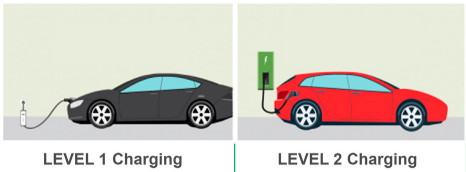
The first thing to consider when picking an EV charger is its charging level. There are two available options for homes: Level 1 and level 2 EV chargers.
Level 1 EV Chargers (up to 2.3kW or 10 Amps)
Level 1 EV chargers are slow chargers that can take up to 50 hours to charge an EV from empty to full. These chargers feature rated power going from 1.0kW up to 2.3kW. A 2.3 kW Level 1 EV Charger, which is the highest rated power option, will take around 21 hours to charge the 50kWh battery of a Tesla Model 3. Since Level 1 EV chargers demand 10 amps or less, they can be used in existing residential circuits, so it’s a simple plug and play.
These portable EV chargers are easily recognised for their compact and easy-to-store design. These chargers feature a control box embedded at some point along the cable going from the Type 2 EV plug up to the electrical plug.
EV drivers who are constantly on the road or who travel a lot, may find portable EV chargers a better fit for their needs. Portable EV chargers are also excellent options for EV drivers lacking the required space or those who do not have a permit to install a dedicated home charger.

Level 2 EV Chargers (up to 9.6kW or 41 Amps)
Level 2 EV chargers are the highest power-rated home charging options. These types of EV chargers feature rated power going from 3.6kW up to 9.6kW. A Level 2 EV charger can get the same 50kWh battery charged in 13 hours for 3.6kW models or in as little as 5 hours for 9.6kW options.
To use level 2 EV chargers it is necessary to install a dedicated electrical circuit that can withstand a high amperage. The specifics for the dedicated circuit vary depending on the charger; a 9.6kW Level 2 EV charger requires a circuit that withstands around 42 amps. This circuit has to be installed by a certified electrician such as one from Revcharge.
Dedicated level 2 EV chargers tend to be the preferred EV charging option for EV drivers who constantly need to charge their car at home. While dedicated EV chargers are not as compact as portable ones, they feature elegant designs that are either wall-mounted or floor-mounted.
Elegance and an aesthetic design are not the only features of dedicated EV chargers. These chargers feature more advanced circuits that give EV owners a wider range of tools to make charging EVs at home easier and more practical (see below section).
Non-Networked or Networked EV Chargers?
When looking for Level 2 home EV charging options it is important to choose between networked or non-networked chargers. In this section, we explain each of them and their most interesting features.
Non-Networked EV Chargers
Portable EV chargers tend to be non-networked, and so are most Level 1 EV chargers. Non-networked EV chargers will normally charge EVs, but they may lack interesting features like charging scheduling, remote monitoring, and others. The bright side is that these chargers are usually cheaper than networked ones and are simpler to get going, and usually are more portable too.
Networked EV Chargers
Networked home EV charging options require an internet connection to deliver most of their additional features, which can be accessed via a mobile or desktop app. Some of the beneficial features included in networked Level 2 EV chargers include the following:
- Real-time monitoring: monitor electrical charging parameters and status updates on the charging process for the EV in real-time.
- Charge schedule: Scheduling charging time for EVs can be extremely helpful. You can optimize the charging to fit Time of Usage (ToU) tariffs. We recommend programming the faster part of the charging process (from 0% to 90%) to match low-peak hours that feature cheaper tariffs.
- Load management: Aside from charging the battery for an EV, advanced EV chargers with bidirectional capability can use a load management function to power a particular load, the home, or deliver power to the grid by using the EV battery as a power source. This means you can power your home from your EV!
- Troubleshooting: Manufacturers can deliver technical support and troubleshoot EV chargers remotely if there are any issues.
Tethered or Untethered EV Chargers?
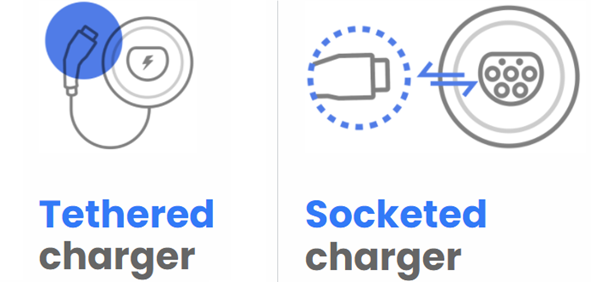
Another important aspect to consider is the decision between a pre-installed cable at the EV Charger or one that comes without a cable. Both options are known as tethered and untethered EV chargers.
Tethered EV Chargers
Tethered EV chargers come with a pre-installed charging cable, featuring a particular EV connector. This cable is sized and designed to withstand the charging current for your particular charger, making it a great initial option for new EV owners.
Purchasing a tethered EV charger is quite common since they do not require you to buy an additional cable. They also do not require that you connect and disconnect the cable regularly, which can be a bit inconvenient to do on a daily basis.
Tethered EV chargers also feature cables with designs and colours matching that of the charger.. The main downside of tethered EV chargers is that they are useless if the cable gets damaged, which means you might be left without power for your EV until it can be repaired. Also, since the cable is already sized for a specific length, you may find the cable to be a little short for charging your car in some instances. Go here to shop our chargers.
Untethered EV Chargers
An untethered EV charger is known as a universal EV charger because the charger can deliver power to any EV without requiring the usage of a particular plug. This charger can fit cables featuring connectors like SAE J1772, Mennekes Type 2, CCS1, CCS2, or CHAdeMO (varies on the charging type) with the most common in Australia being the Mennekes Type 2 cable. Another advantage is using the same cable you use at a public charge point, which saves some money in the process.
Untethered EV chargers are also future-proofed. These EV chargers allow you to buy any new EVs featuring a different charging port, without this being a problem. They are also convenient in case the cable gets damaged, because instead of rendering the unit useless, you would only need to buy a new cable and the problem is solved. Additionally, another great advantage is that you can choose a cable with the ideal length for your needs, meaning that you can choose longer charging cables than the default ones that come integrated with a tethered charger. There are multiple untethered EV charger options available such as the Wallbox or the Zappi models.
Dedicated Electrical Circuit for EV Charging at Home
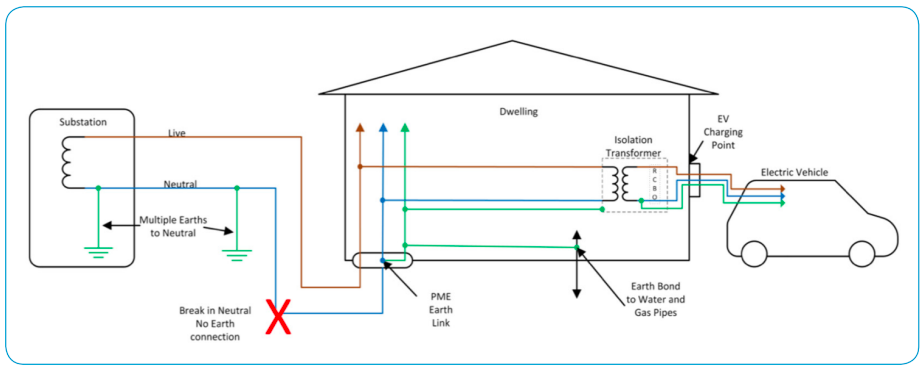
Installing dedicated electrical circuits are required to deliver the current that level 2 EV chargers demand. These circuits have to comply with the Australian Electrical Standards (AS/NZS 3000:2018). The usual process is as follows:
- A certified electrician assesses the power capacity and load of the home.
- Different EV charging alternatives are considered until a device is chosen.
- The circuit is installed. This means running the AC wire, installing protection systems, and verifying the earthing.
- EV charger is installed.
- Some electricity suppliers require filling an Electric Work Request (EWR) to install a dedicated meter for the charger. You have to wait until the meter is installed and active.
- After all previous steps are done, you can finally charge your EV at home.
- You can also charge your evs through solar battery system.
Read also: Myths and Facts about Electric Vehicles
revcharge is an end-to-end EV charging service provider. We take the stress and guesswork out of not only finding an EV charger that meets your needs, but that too of organising a trained technician to install and activate your system. Every EV charger on offer has been carefully evaluated for its performance and features by our specialised team.
Our goal is to save you time and money, while ensuring a quality install that will last you for years to come. All you have to do is answer some quick questions about your home and electric car and send us photos of your switchboard and preferred charger location. We’ll take care of the rest!
Learn more here and get an obligation-free quote today!